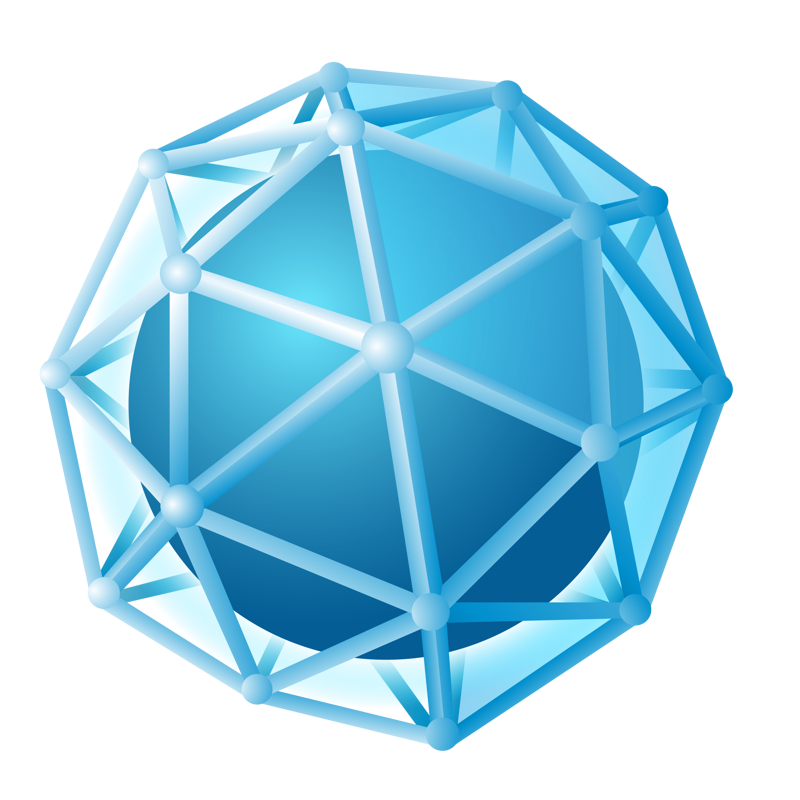
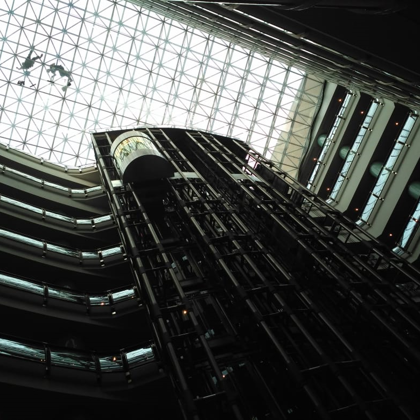
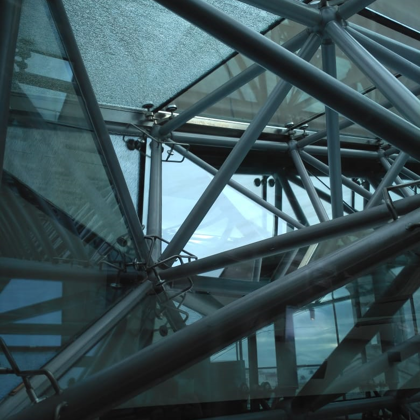
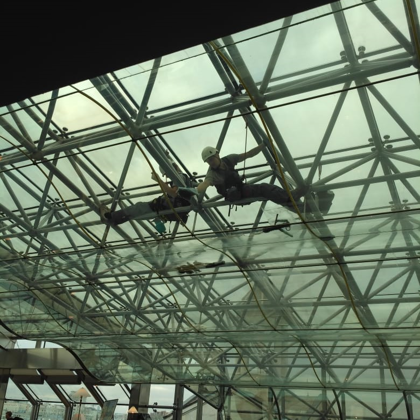
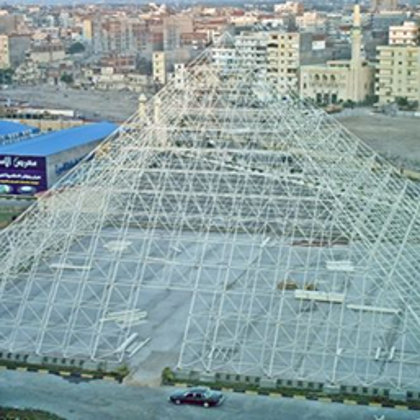
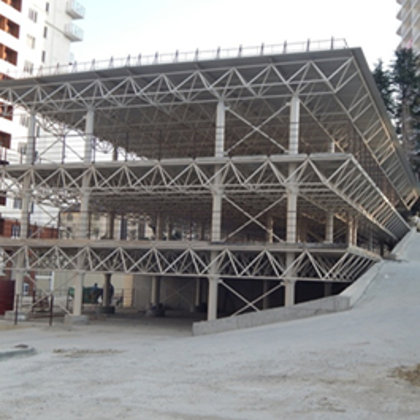
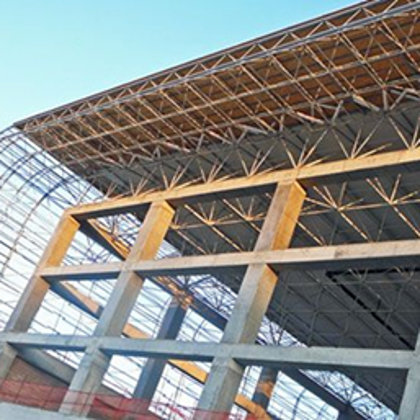
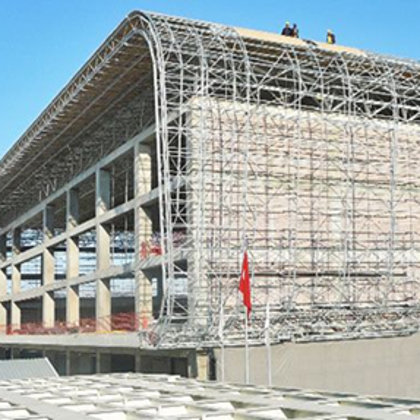
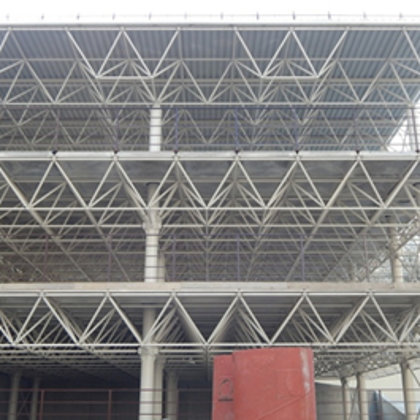
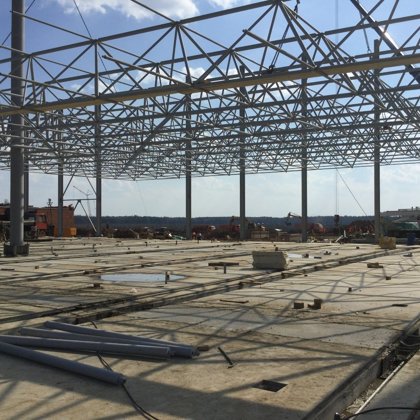
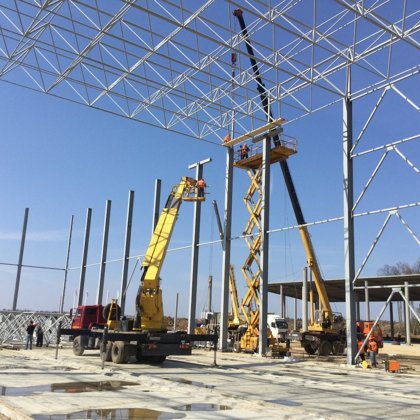
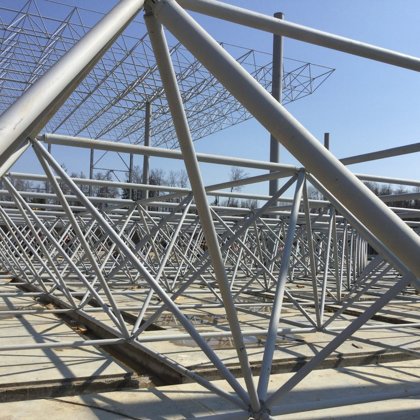
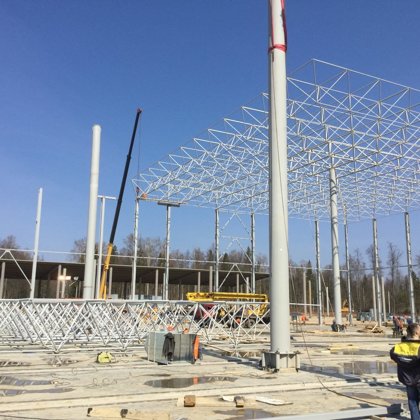
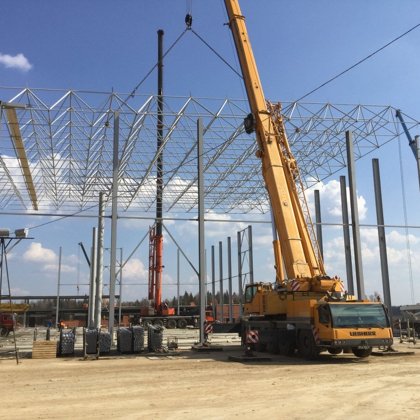
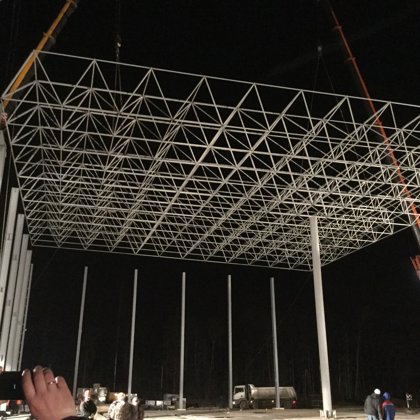
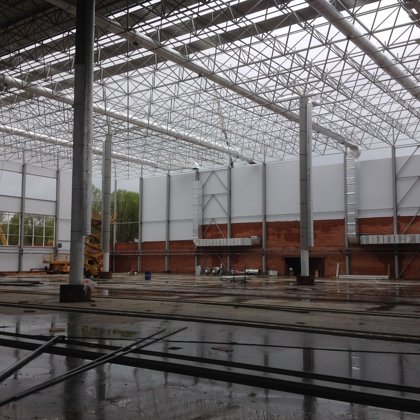
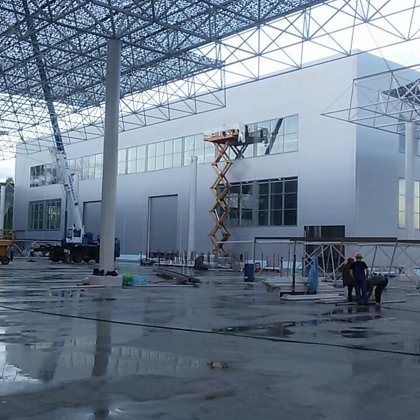
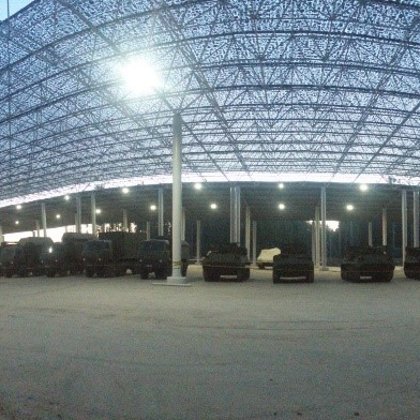
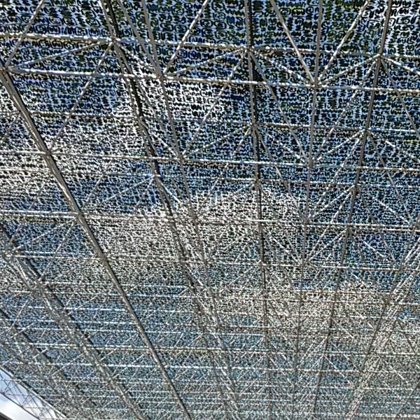
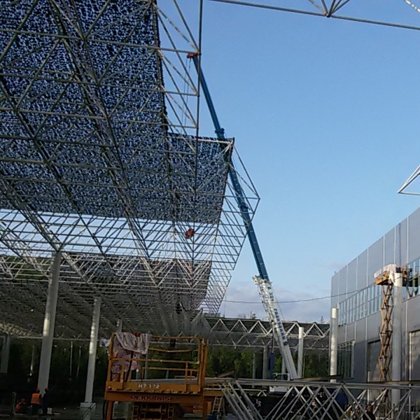
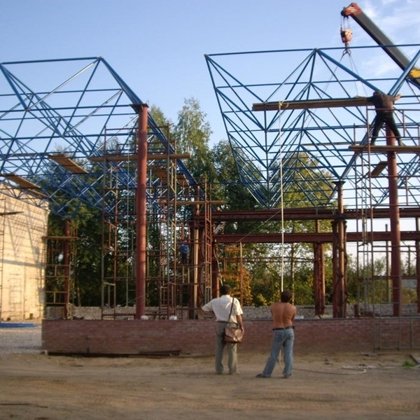
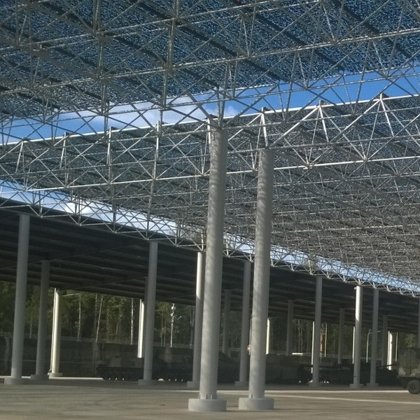
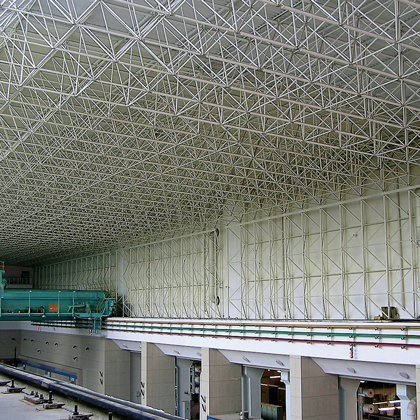
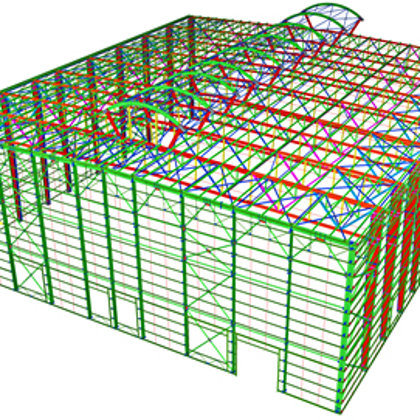
Spatial structure refers to a structure made of an assemblage of linear members interconnected to each other in space, resisting loads applied at their connections or along their lenghts.
The design of spatial structures is a collaborative effort between architect
and engineer, which typically begins at early stages of the conceptual design.
The geometry types, module sizes, support conditions, materials, and design
approach are not determinated at the early stages of the design of spatial
structures. The members of spatial structures are interconnected, they can
distribute loads effectively. This means tat a concentrated load applied at a
point on the structure can be resisted by members a large distance from it.
ADVANTAGES
- Due to the low self-weight of these structures, the total costs of foundations and
columns are relatively small. The system is light and more efficient as
materials are used more optimally than in other conventional systems.
- Spatial structures can be assembled in a shop and transported to the site
erection. They require less material then other conventional linear systems
and, therefore, if prefabricated can be an economical long span structural
system. The assembly and erection are easy and fast, requiring unskilled labor.
- The manufacturing of the connections (or nodes) is one of the most important
factors in cost-effectiveness of spatial structures. An ideal connector can be
easily mass produced, used to join members at various angles, and resist the
forces acting on it.
- Due to the low self-weight of these structures, the total costs of foundations
and columns are relatively small.
- Spatial structures can be assembled in a factory and transported to the site
erection. They can be easily assembled and erected using a number of modular
units.
- Using spatial structures for large span systems can provide 15 – 30 % reduction
in the amount of the wieght as compared to other long span structural systems.
- They are highly redundant and statically indeterminate systems. As a result, a
failure of a member does not result in the complete collapse of the structure.
- They are a significant advantage in terms of the fire resistance as compared to
conventional planar structures.
They are very durable when subjected to fire. - They are easily expandable and demountable with the flexibility of placing
supports at various locations.
Supports can be removed or relocated without endangering the overall structural stability. - Various regular configurations are architecturally appealing and for this
reason almost all spatial structures are architecturally exposed.
- Flexibility in support locations. Spatial structures can be supported at any
node.
This is advantageous for interior architectural planning.
SERVICES
Design of the load-bearing structures:
- Metal structures;
- Reinforced concrete structures;
- Wooden structures;
- Composite structures;
- Technical documentation for construction and production.
Detailed design of construction schemes and elements:
- Assembly schemes;
- Detailed drawings of assembly details and elements.
Design for individual technical equipment:
- Sketch design and technical drawings;
- Detailed drawings for a whole construction, individual elements and details.
Various professional services for manufacturers:
Standardized solutions for designing and production;
- Standardized product and node catalogue production and formalization;
- Personalized standard production for organizations or business purposes;
- Engineer’s supervision of the production and assembly of structures;
- Engineer’s supervision for the production and assembling of individual
technical equipment.
TECHNOLOGIES
Wide oppurtunities for different format documents to prevent errors and
weaknesses for construction and assembly process:
- 3D modelling of bearing structures and architectural solutions;
- 2D drawing in different formats;
- Drawings and digital documents;
- Drawings in acceptable digital format;
- File preperation in accordance with the requirements.
Types of metal structures:
- Traditional roof and farm structures;
- Facilitated cross-section steel structures;
- Spatial grid structures;
- Variable cross-section structures;
- Frame multiplicity;
- Spatial structures from pipes of different cross-sectional diameters.